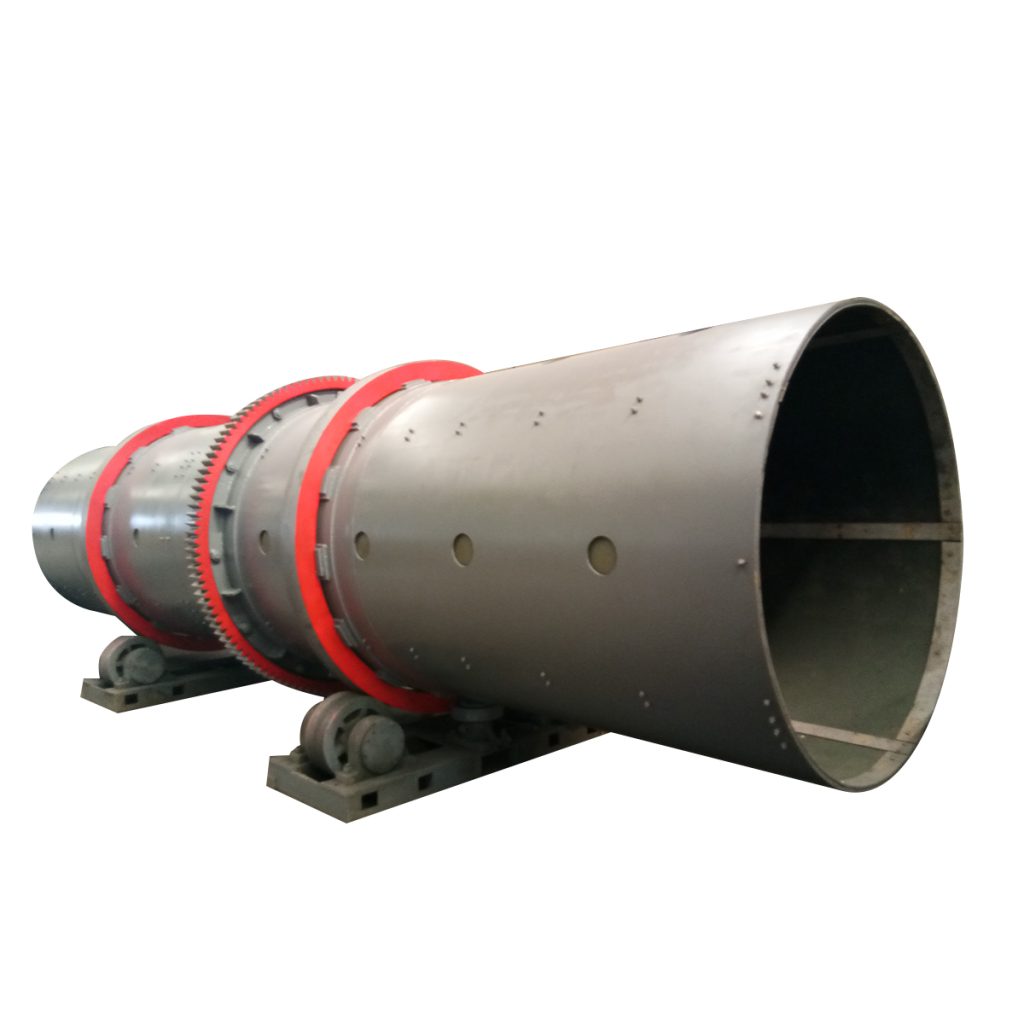
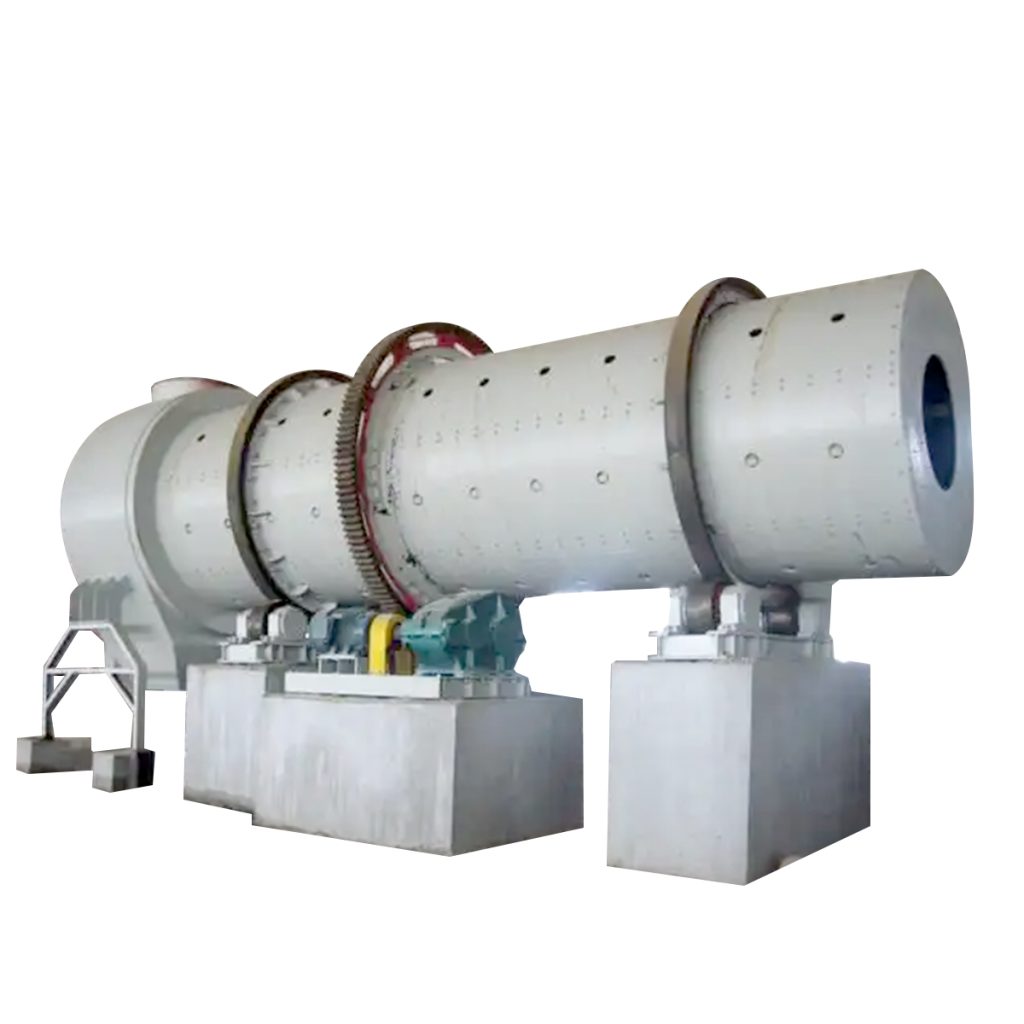
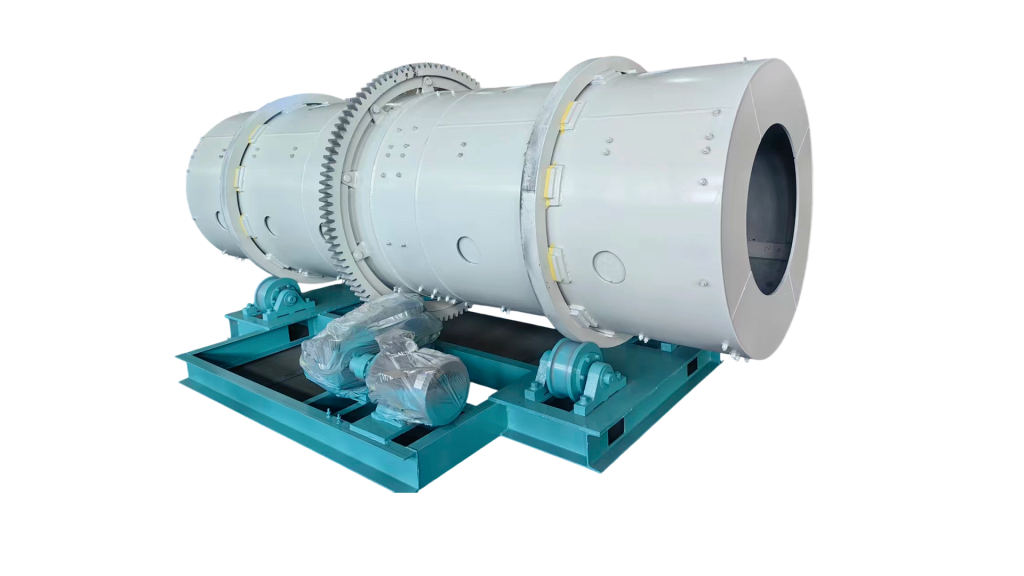
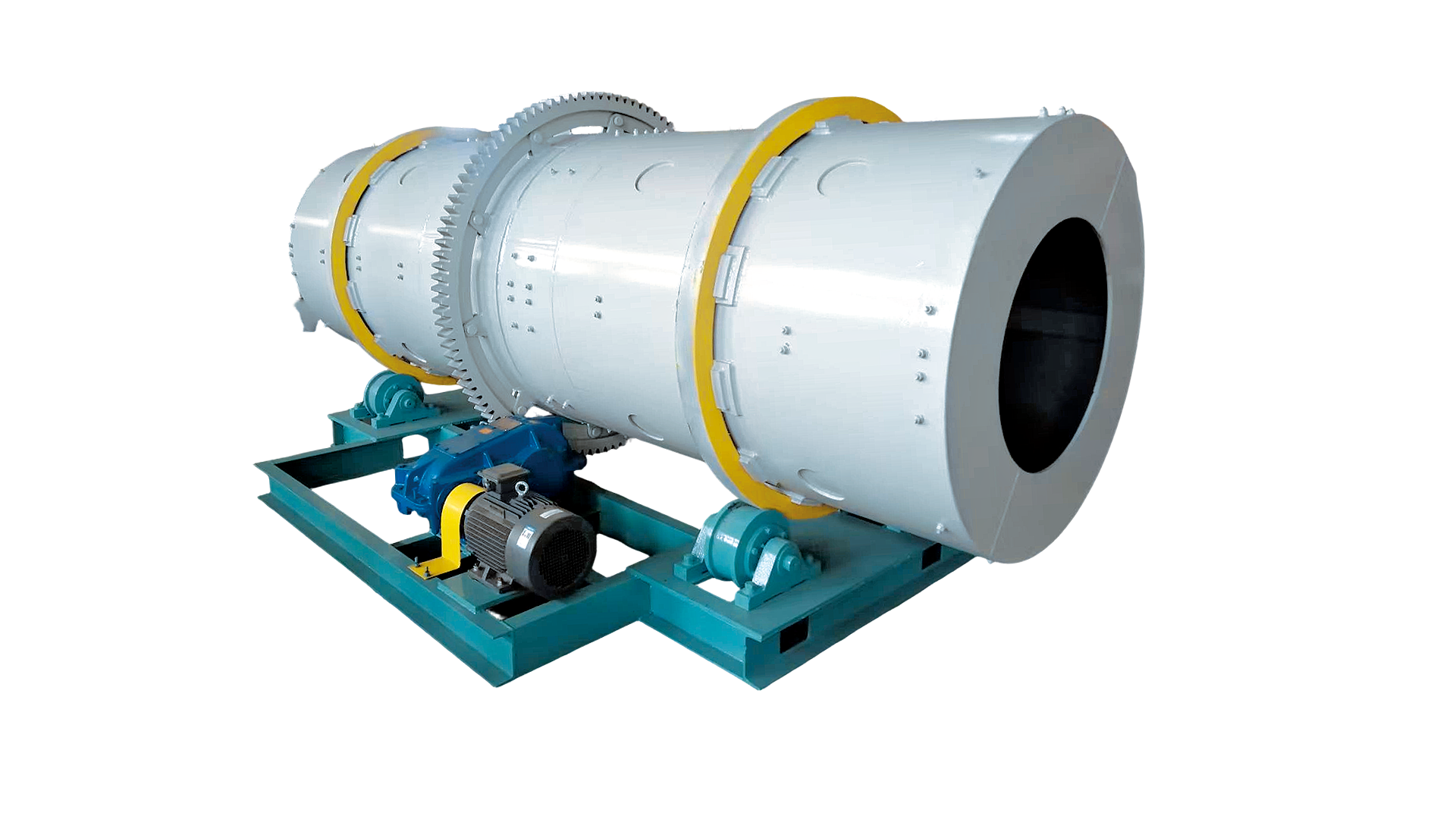
The Rotary Drum Granulator is a specialized molding machine designed to process powdered or slurry materials into spherical granules. It is widely utilized for large-scale production in fertilizer, chemical, and other industrial sectors.
General Overview
Primary Function: Manufacturing of spherical granules.
Production Capacity: 3 – 45 t/h .
Granule Size: 2 – 10mm.
Applicable Raw Materials: Highly adaptable to diverse materials, including organic waste (livestock manure, straw, sludge), base fertilizers (N, P, K), and various additives. It is suitable for producing compound, organic, bio-organic, and controlled-release fertilizers.
Technical Description & Features
The machine transforms powdered materials into spherical pellets through a rotating mechanism.
- Major Components: Support rollers , transmission unit, large gear, rolling rings, drum shell, feeding device, spraying system, hot air system, and retaining rings.
- Key Specifications:
- Diameter: 1.4 – 3.2 m.
- Structure: Robust and durable design, simple operation, low maintenance costs, high output, and high pelletizing efficiency.
- Materials: Available in various materials, including optional stainless steel for corrosion resistance.
Applications & Advantages
A.Large-scale Production of Compound & Organic Fertilizers
Utilizes steam heating or cold granulation processes to handle high, medium, and low-concentration compound fertilizers. In sulfur-based compound fertilizer production, ammoniation granulation uses the heat of neutralization to evaporate moisture.
- Advantages: Uniform nutrient distribution and high granule strength.
- Organic Sector: Directly processes fermented manure, straw, and biogas residue into organic fertilizer using wet-agglomeration technology.
- Results: Pelletizing rate exceeds 70%, with small-sized, recyclable return materials.
B. Synergistic Granulation of Bio-Organic-Inorganic Fertilizers
- Supports the blending of organic waste (e.g., sugar refinery filter mud, paper mill sludge) with inorganic nutrients.
- Advantages: Capable of producing large-sized slow-release fertilizer granules.
C. Chemical & Environmental ApplicationsConverts food processing residues (soybean dregs, vinasse) and municipal sludge into granular fertilizer.
- Environmental Impact: Reduces pollution and achieves resource recycling.
- Chemical Industry: Processes phosphate rock powder and potash salts into products like Calcium Ammonium Nitrate and Diammonium Phosphate (DAP). Especially suitable for ambient temperature granulation of heat-sensitive materials.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the working principle?
The powdered or pasty material enters the inclined rotating drum. As the drum rotates, the material tumbles and rolls continuously. Through a sprayed atomized binder or the material’s own viscosity, fine particles aggregate into larger cores. Driven by friction, centrifugal force, and gravity, these particles collide and compress into high-strength spherical granules before discharging.
Q2: How to solve insufficient granule strength?
Moisture Control: Strictly regulate moisture content based on material properties (typically between 20% – 30%).
Thermal Management: Optimize the heating or cooling system to ensure ideal internal temperatures.
Dwell Time: Adjust drum speed or increase the height of the retaining ring to extend the material’s residence time for better compaction.
Q3: How to solve uneven granule size?
Formulation: Optimize the material ratio for consistent physical properties.
Feeding: Check the feeding device and adjust the speed to ensure a uniform flow.
Speed Regulation: Adjust the drum speed (usually between 5 – 15 r/min) based on requirements.Binder Control: Precisely control the binder dosage through experimental testing.
Q4: What causes clogging and how to fix it?
Causes: Excessive feeding speed;High material viscosity leading to buildup; Poor discharge port design or foreign object blockage.
Solutions: Reduce feeding speed to match capacity;Pre-treat viscous materials (reduce moisture or add dispersants); Optimize the discharge structure and perform regular cleaning.
| Model | Rotary Drum | Production Capacity | Overall Dimensions L×W×H | ||||
| Inclination Angle | Inner Diameter | Length | Rotation Speed | Power | |||
| ° | mm | mm | r/min | Kw | t/h | mm | |
| ZG1405 | 2-2.5 | 1400 | 5000 | 14 | 7.5 | 3-8 | 5000*1950*2100 |
| ZG1606 | 2-2.5 | 1600 | 6000 | 11.5 | 11 | 5-8 | 6000*2100*2400 |
| ZG1807 | 2-2.5 | 1800 | 7000 | 11.5 | 18.5 | 8-10 | 7000*2200*2800 |
| ZG2008 | 2-2.5 | 2000 | 8000 | 11 | 22 | 10-15 | 8000*2600*3200 |
| ZG2210 | 2-2.5 | 2200 | 10000 | 10.5 | 37 | 15-20 | 10000*2800*3400 |
| ZG2410 | 2-2.5 | 2400 | 10000 | 9 | 45 | 20-25 | 10000*3220*3900 |
| ZG2610 | 2-2.5 | 2600 | 10000 | 8.3 | 55 | 25-30 | 10000*3500*4200 |
| ZG3010 | 2-2.5 | 3000 | 10000 | 8.3 | 75 | 30-35 | 10000*3900*4600 |
| ZG3210 | 2-2.5 | 3200 | 10000 | 8.3 | 90 | 35-40 | 10000*4100*4800 |