Description
Product Introduction
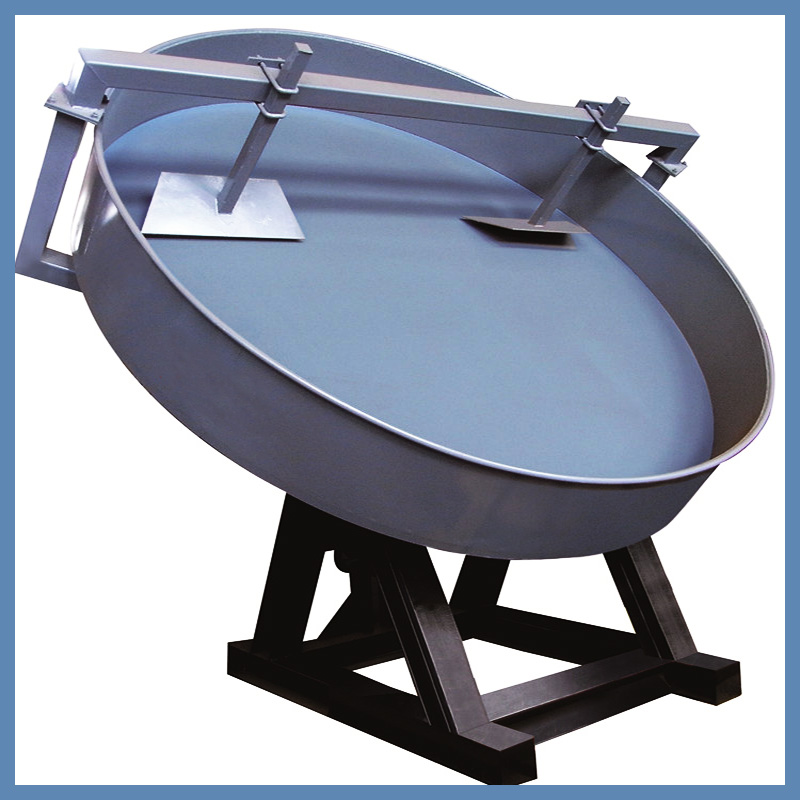
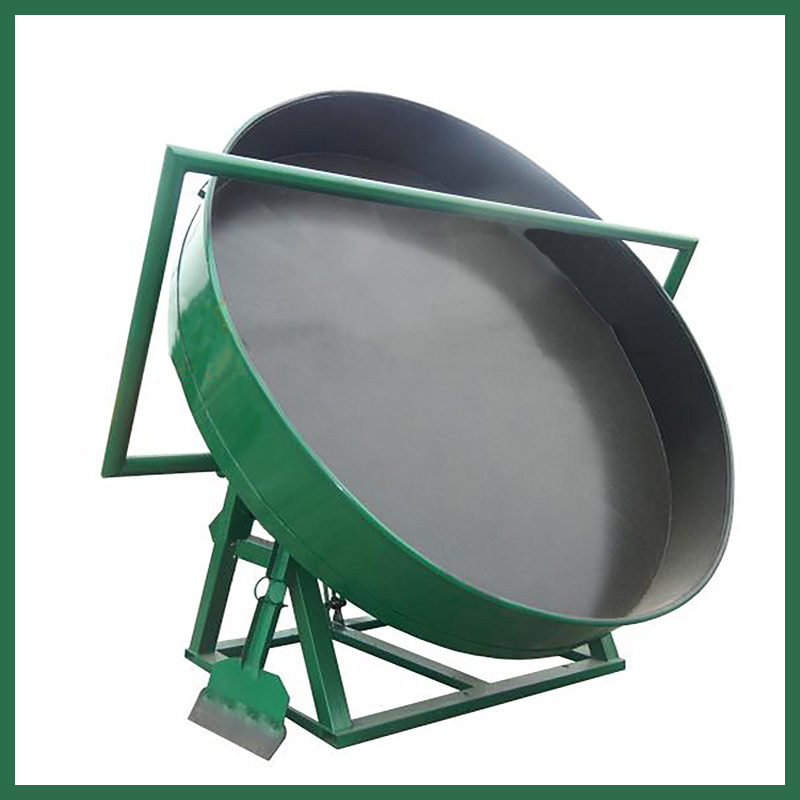
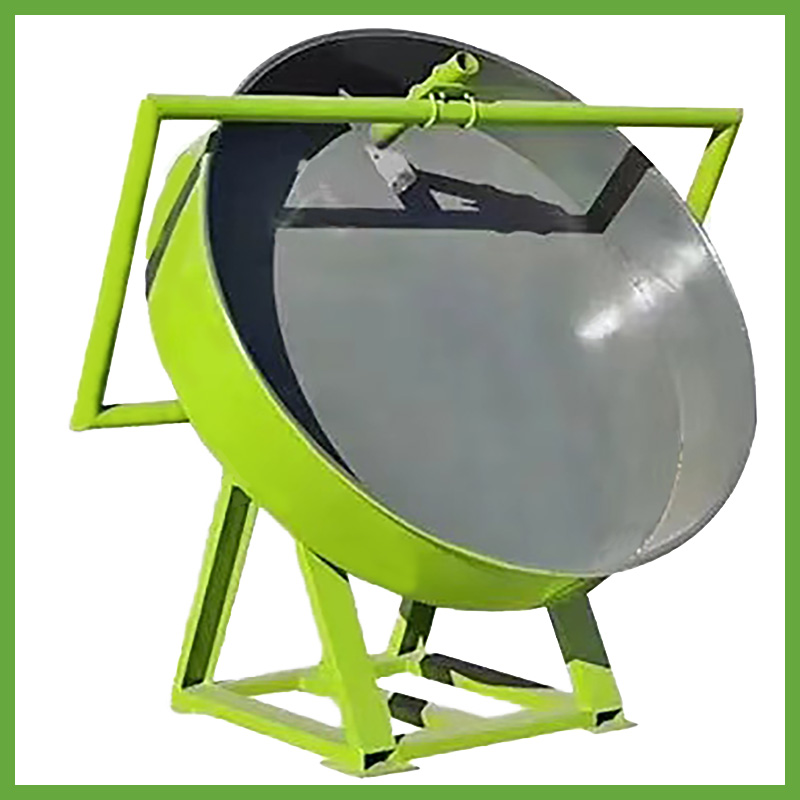
The Disc Granulator (Pan Granulator) is a volumetric sizing equipment that shapes powdered materials into spherical granules through the rotation of an inclined disc. Due to its low investment cost, intuitive operation, and easy maintenance, it plays a vital role in processing organic fertilizers, compound fertilizers, coal dust, and various other powders.
- Core Components: Primarily consists of the main pan (disc), large gear, transmission unit (motor/reducer), base frame, scraper assembly, and spray system.
- Physical Appearance: Characterized by a massive disc with an adjustable inclination angle; the pan bottom is typically reinforced to handle heavy loads.
- Applications: Ideal for granulating NPK compound fertilizer powders or organic fertilizer powders, particularly for small-to-medium-sized production lines.
Performance Characteristics
- High Granulation Rate: The arc-shaped disc structure allows for a granulation rate of over 93%, significantly minimizing material recycling.
- Precise & Flexible Adjustment: The inclination angle is typically adjustable between 40° and 60°. Combined with variable rotation speeds, this allows for precise control over the final granule size.
- Robust Durability: The pan bottom is reinforced with multiple radiating steel plates and often lined with stainless steel plates. This prevents material adhesion and extends the equipment’s service life.
- Stable Operation: Equipped with a flexible belt drive between the motor and reducer, ensuring a smooth start-up and reducing mechanical impact on components.
- Superior Granule Quality: Produces well-rounded spherical granules. The inherent “natural classification” function ensures highly uniform particle size distribution.
Working Principle
The operational logic of the Disc Granulator can be summarized as “Centrifugal Tumbling + Spray Nucleation + Rolling Growth”:
- Feeding & Wetting: Raw powder enters the high-speed rotating disc. An overhead spray system misted with a liquid binder (usually water or a chemical liquid) wets the powder to form tiny “nuclei.”
- Rolling Growth (Snowball Effect): Due to the disc’s inclination and rotation, friction and centrifugal force carry the material to the highest point. Gravity then causes it to roll back down the face of the pan. Through this repetitive motion, the granules capture surrounding dry powder and grow larger, similar to the process of rolling a snowball.
- Automatic Classification & Overflow: As granules grow larger and heavier, the centrifugal force acting on them changes. Qualified large granules float to the surface and migrate toward the lower rim of the disc. Finally, finished spheres that reach the preset size automatically overflow from the disc’s edge.
- Wall Cleaning: Integrated scrapers (powered or non-powered) continuously clean the bottom of the pan to prevent buildup and facilitate material circulation.
Techspecs:
| Model | Diameter | Disc | InclinationAngle | Power | Production Capacity | OverallDimensions (L×W×H) | |
| Rim Height | RotationSpeed | ||||||
| mm | mm | r/min | ° | Kw | t/h | mm | |
| YP2645 | 2600 | 450 | 16.7 | 40-60 | 7.5 | 1-2 | 2600*2000*2600 |
| YP2845 | 2800 | 450 | 14 | 7.5 | 3-4 | 2800*2200*2800 | |
| YP3048 | 3000 | 480 | 13 | 11 | 4-5 | 3000*2500*3000 | |
| YP3250 | 3200 | 500 | 12 | 11 | 5-7 | 3200*2800*3200 | |
| YP3550 | 3500 | 500 | 11.5 | 15 | 7-9 | 3600*3200*3500 | |
| YP4055 | 4000 | 550 | 11.5 | 18.5 | 9-10 | 4100*3400*4000 | |
| YP4555 | 4500 | 550 | 11.5 | 22 | 10-12 | 4600*3700*4500 | |
| YP5055 | 5000 | 550 | 10.5 | 22 | 10-15 | 5100-3800*5000 | |